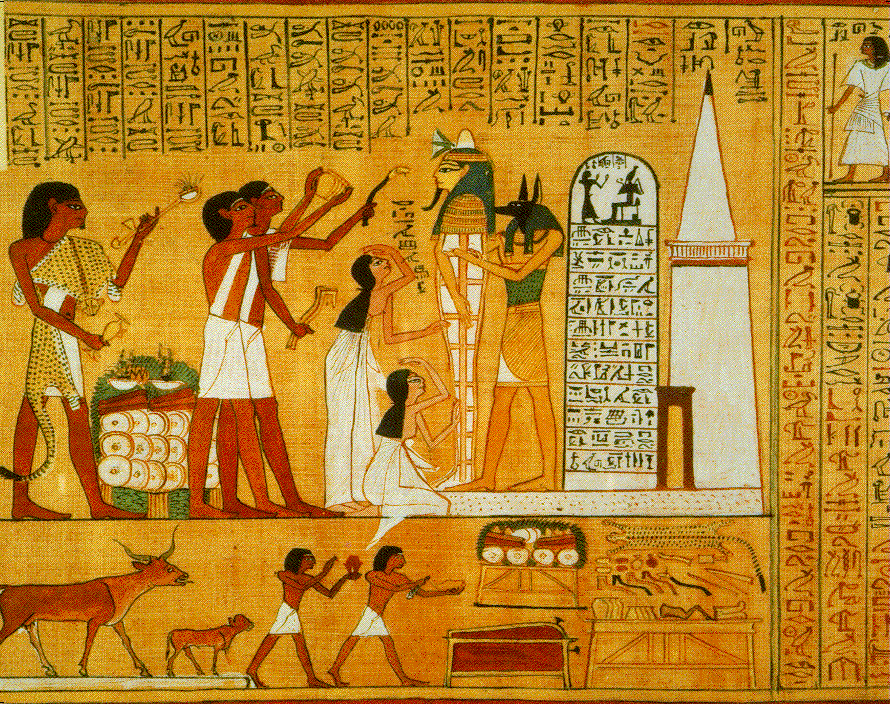| Links
|
pictures |
vocabulary |
unit plan | comprehension |  |
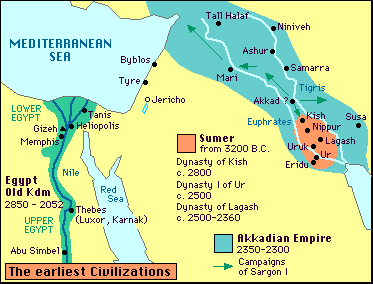
EGYPT
WHERE DID THE ANCIENT EGYPT DEVELOP?
- A country with 3,000 years of history.
The territory that ancient Egypt occupied is located along the River Nile. During most of its course, the river goes through a narrow valley, Upper Egypt. A little before it empyies into the sea, the river opens into a wide delta, Lower Egypt.
- The Egyptians and the Nile.
The ancient Egyptians lived in lands which were situated on the banks of the river Nile, because these were the only fertile lands. In summer, the Nile waters rose, overflowed and flooded the fields. When the waters moved back, they left slime which was very fertile for cultivation. On the contrary, both sides of the River Nile would be occupied by wide, arid and unihabited deserts.
In order to benefit from the waters of the Nile, the Egyptians built dams to hold back the waters of the river, and canals, which carried water to the farthest arable lands.
The River Nile was also the main means of communication. Sailing ships went along the river to transport both people and goods.
HOW WAS EGYPT RULED?
- The pharaoh ruled Egypt
The Egyptians called their king pharaoh. The pharaoh was all powerful: he passed laws, governed the country, owned most of the lands, controlled trade and led the armies.
The Egyptians believed that the pharaohs were gods.
Noblemen and priests.
The most important posts in Egypt were held by noblemen and priests.
- The noblemen were memebers of the pharaoh's family, and they possessed great part of the land and herds colossal fortunes.
- The priests controlled the religious rites. They had thousands of people at their service.
- The scribes were people who could read, write and count. They were responsible for writing official documents, as well as for keeping account of the royal taxes and the goods that went in and out of the pharaoh's palace. These civil servants enjoyed great prestige and a good economic position.
HOW DID THE MAJORITY OF THE POPULATION LIVE?
- Peasants. Nine out of every ten Egyptians were male and female peasants. They lived poorly in small mud-brick houses along the River Nile.
Peasants cultivated tha lands belonging to the pharaohs, the temples and the noblemen. In exchange for their work, they were given a part of the harvest, but they had to give anaother part to the landowners. They could hardly make a living.
- Craftsmen. The main craftmen were stone carvers, sculptors, goldsmiths and papyrus and linen manufacftures. The majority of them worked for the pharaoh.
- Merchants. They sold products. Since there were no coins in Egypt at that time, they used barter, that is to say that they exchanged some products for others.
- Slaves. The slaves were people who had no rights. Generally, they were prisoners of war. Most of them were owned by the pharaoh, although priests and noblemen also possessed slaves. The pharaoh used them for building great monuments, working in copper mines or as soldiers in the army.
WHAT WAS THE EGYPTIAN RELIGION LIKE?
- The Egyptians were politheistic.
The Egyptians were politheistic. The principal god was the sun, called Ra. Other important gods were Isis, Osisris, Horus and Thot. The Egyptians worshipped certain animals such as the crocodile; natural elelments, such as the Earth or the River Nile, and people, such as the pharaoh.
Temples: places of worship
The Egyptians believed that religious rites were necessary to preserve the order of the universe: the location of the stars in the sky, the succession of the seasons or the annual floods of the Nile. For this reason, it was essential to have a body of priests for each god and a great temple to keep the statue of the godwhere he could be worshipped.
The statue of the god was located in the sanctuary. Only the priest and the pharaoh could enter the temple and pray to the god. On the god's feast day the priests took the statue out in procession.
- The Egyptians believed in immortality.
The Egyptians believed in life after death. In order to preserve the bodies of dead people for their new life, the Egyptians turned them into mummies. Then they put the mummies into a sarcophagus and buried them in tombs.
The sarcophagus was surrounded by a treasure.
The tombs: pyramids and hypogea.
The first pharaohs were buried in enormous stone pyramids. Inside the pyramid there was a funeral chamber, the room where the body of the dead pharaoh and his treasure were placed. The most famous pyramids are those at Giza, in which pharaohs Khufu, Khafra amd Menkaura were buried about 5,000 years ago.
Later on other types of tombs, called hypogea, were built. These were tombs excavated inside a mountain, whose entrance was camouflaged to protect them from thieves.
The jackal god Anubis
VOCABULARY
Linen: Egyptian fabric made from a plant called flax.
Papyrus: Kind of Egyptian paper made from a plant also called papyrus.
Worship: Series of religious practices and rites to honour a god.
Rite: a ceremonial act or series of acts.
Pyramid: . A massive monument of ancient Egypt having a rectangular base and four triangular faces culminating in a single apex, built over or around a crypt or tomb
Hypogea: A subterranean chamber of an ancient building.
Mummy: The dead body of a human or animal that has been embalmed and prepared for burial, as according to the practices of the ancient Egyptians
Hieroglyphics: Of or relating to representation by drawings or pictures:
- graphic, illustrative, photographic, pictographic, pictorial