| Links
|
pictures |
vocabulary |
comprehension | unit plan |  |
THE FIRST CIVILIZATIONS
- The appearance of writing.
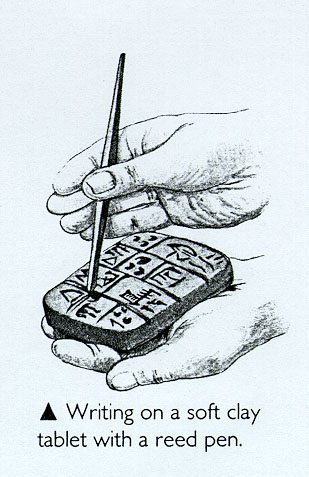
Writing appeared in Mesopotamia over 5,000 years ago. When cities grew, it became necessary to create a system of control to keep the data which were of interest to the king and his government: taxes, trade transactions, etc.
Soon the first holy books, science books and literary works arose.
The invention of writing was so important that it is from this event that historians set the birth of History.
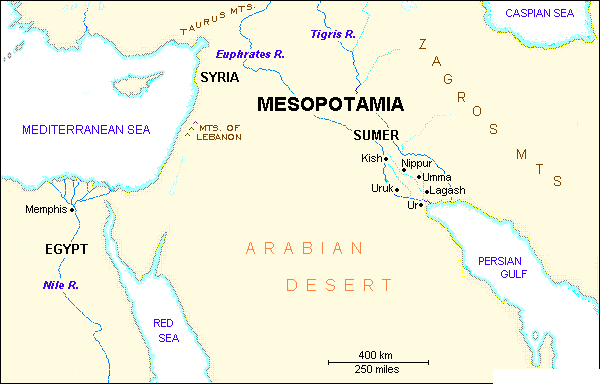
- The first civilizations.
The first civilizations emerged in Mesopotamia, Egypt, India and China about 5,000 years ago. They are called river civilizations because they developed along the banks of large rivers:
- The Tigris and Euphrates in Mesopotamia
- The River Nile in Egypt
- The Indus River in India
- The Yellow and Blue rivers in China
Rivers civilizations were characterised by:
- Strong political power. This power was centred on a king. Kings created a body of civil servants and formed large armies.
- A very hierarchical society. Society was divided into groups very well differentiated:
- Privileged people, who was a minority and owned most of the lands.
- A majority of subjugated people.
- A great artistic development.
HOW DID THE FIRST EMPIRES EMERGE?
Kings became very strong and formed large empires.The enlargement of territories brought the need to create a state structure. So they assigned governors to rules the farthest provinces. They also created a body of servants, who could write, read and count, and they collected taxes.
To regulate the relations between inhabitants, the first codes of law were created, for example, the code of Hammurabi.
What was society like in the first civilizations?
The first urban societies.
From the third millenium BC, cities grew a lot. Cities experienced a clear division of work. Each person was devoted to a particular job and buy other necessary things at the market.
Cities had to buy some food, raw materials and luxury products in remote regions. This is why trade adquired a great importance. None of these civilizations had coins, they used barter, which consisted of interchange of products.
The cities of Mesopotamia were surrounded by walls of sun-dried bricks. There were two buildings inside them: the temple and the palace.
Privileged groups had all the rights and possessed most of the riches.
- The aristocracy consisted of the king, his family and the nobility. They possessed great part of the land.
- The priests were in charge of the religious rituals. They possessed part of the land and co-operated with the government.Temples were the gods' resedence on Earth. They were built on a tower of several stages, called ziggurat.
- The scribes stood out amomg the civil servants. They came from noble families and had a great power.
The rest of the people could be free, if they had rights, or slaves, who had no rights were treated as objects.
- Peasants rented the lands that surrounded the city and belonged to the king or the temple. In exchange, they had to give them part of the harvest.
- Craftsmen worked in workshops.
- Mesopotamian art
In Mesopotamia, both architecture and sculpture were of a high quality.
- In architecture, the materials used for construction were brick and adobe. Mesopotamians invented the arch and the vault. They built splendid palaces, such as that of Khorsabad; monumental gates, such as the Ishtar Gate; and great temples, such as that of Marduk, in Babylon. The Mesopotamian buildings were decorated with coloured clay strips and beautiful reliefs and frescos.
- For sculpture, they used stone. Summerians and Akkadians built statues of theis kings and gods. Assyrians made great figures of bulls with human heads, and expressive reliefs with hunting and war scenes.
Would you like to know the activity that a Mesopotamian student carried out during the day? Click here and do this exercise.
The contributions affecting the modern world from our ancient ancestors in Mesopotamia are numerous. The ancient Sumerians created the world's first civilization where people settled together in one area known as the city-state. For this accomplishment, ancient Mesopotamia is often referred to as the "cradle of civilization."
Another contribution vastly affecting the modern era was the Sumerians' creation of a writing system. Although we do not use the same writing system today, it spawned the many different writing models that led to today's writing.
Other inventions include the water clock, the twelve-month calendar based on lunar cycles, the wheel, the plow, and the sailboat. All these inventions improved the daily life of the Sumerians.
CUNEIFORM WRITING
HAMMURABI
HAMMURABI CODE
NANNA ZIGGURAT
ZIGGURAT
ISHTAR GATE
GUDEA
STELA OF NARAM-SIN
BULL-MAN FROM KHORSABAD
WOUNDED LION
VOCABULARY
Mesopotamia: Mesopotamia means "the land between the rivers" or "the land between the two rivers." This was the site of the world's first civilization, Sumer.
Cradle of civilization: Mesopotamia is often referred to as the "cradle of civilization" because the world's first civilization occurred there.
Sumer: Sumer was the world's first civilization. It was located in the southern area of Mesopotamia where the twin rivers converged. The people who lived in this area were called Sumerians.
Ziggurat: The ziggurat was a temple. It was located in the center of each Sumerian city-state.It housed the city-state's patron god. The term ziggurat means "mountain of god" or "hill of heaven." Since the ziggurat was a sacred place, only priests could enter it.
Cuneiform: The ancient Sumerians created the world's first writing system known as cuneiform. The term cuneiform means "wedge-shaped." Sumerian writing is wedge-shaped because of the the type of instrument that was used to create it.
Scribe: After graduating from a Sumerian school, a young man became a scribe, or a writer.
Empire: An empire is a collection of kingdoms under the power of one powerful ruler.
Arch: Curved structure that can be supported by two pillars or bridge the gap of a wall which normally serves as prop.
Fresco: Pictorial technique which consists of applying colours on a surface made of layers of fresh plaster.
Relief: Sculptural technique in which shapes project out from the scene.
Vault: Arched structure which covers the space between two walls or several pillars.





