|
Links |
pictures |
vocabulary |
unit plan |  |
PREHISTORY

We call
Prehistory the period between the origin
of the human being and the invention of writing, about 6,000 years ago.
This period is divided into three
stages: the Palaeolithic Age, the Neolithic Age and the Metal Age. ![]()

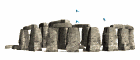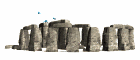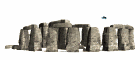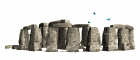
* The Neolithic Age began about 10,000 years ago, when human groups started to live in villages and practise agriculture and cattle raising.
* The Metal Age began about 7,000 years ago, when human beings learnt to use metals to make objects.


* Australopithecus were the first ancestors of the human being and appeared about five million years ago. They were very similar to chimpazees. They first appered in Africa.
* Homo habilis appeared two million years ago.
They already made tools of stone and lived on hunting and gathering.
* Homo erectus appeared a million and a half
years ago. They were very similar to
Homo habilis, but they had a greater technological development.
For example, this species discovered fire. Their remains have been found
in Asia, Europe and Africa.
*
Homo sapiens appeared about
100,000 years ago. There are two subtypes:
Neanderthal man, similar to us
but more sturdy, and Homo sapiens
sapiens, the species we belong to. Their remains have been found
in Autralia and America
. ![]()
![]()

Characteristics of the human species:
Human beings have in common some characteristics:
* The biped walk, so their hands are free to work.
* The opposable thumb, that lets us make manual labours.
* The development of language.

 Bison in the cave of Altamira
Bison in the cave of AltamiraMen hunting in Castellón

 Palaelolithic
tools
Palaelolithic
tools  Venus of Willendorf
Venus of Willendorf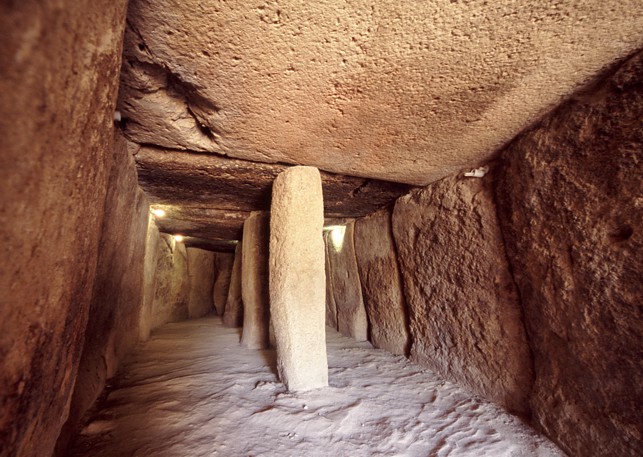
Dolmen in Antequera
 Naveta
Naveta  Taula
Taula  Stonehenge
Stonehenge Vista aérea de Stonehenge
Vista aérea de Stonehenge
VOCABULARY
Hominization: The evolutionary process leading to the development of human characteristics that distinguish hominids from other primates.
Prehistory: History of humankind in the period before recorded history.
Palaelolithic: Of or relating to the cultural period of the Stone Age until the beginning of the Mesolithic Age.
Neolithic: Of or relating to the cultural period of the Stone Age, characterized by the development of agricultural and making of polished stone implements.
Rupestrian: Made of, or written on rock.
Cavern: A long cave.
Predator: One that victimizes, plundres, or destroys, especially for one's own gain.
Biface: Generic term for any stone tool that has been flaked on both faces of the stone.
Booster: A device for increasing power or effectiveness.
Sedentary: Remaining or living in one area, not migratory.
Nomad: A member of a group of people who have no fixed home and move according to seasons from place to place in search of food and water.